Documentation Style Guide
This document defines the standards for GitLab documentation, including grammar, formatting, word use, and more.
For style questions, mention @tw-style in an issue or merge request. If you have access to the GitLab Slack workspace,
use the #docs-processes channel.
In addition to this page, the following resources can help you craft and contribute to documentation:
- Doc contribution guidelines
- Recommended word list
- Doc style and consistency testing
- UI text guidelines
- GitLab Handbook style guidelines
- Microsoft Style Guide
- Google Developer Documentation Style Guide
- Recent updates to this guide
Documentation is the single source of truth (SSOT)
The GitLab documentation is the SSOT for all information related to GitLab implementation, usage, and troubleshooting. It evolves continuously, in keeping with new products and features, and with improvements for clarity, accuracy, and completeness.
This policy prevents information silos, making it easier to find information about GitLab products.
It also informs decisions about the kinds of content we include in our documentation.
The documentation includes all information
Include problem-solving actions that may address rare cases or be considered risky, but provide proper context through fully detailed warnings and caveats. This kind of content should be included as it could be helpful to others and, when properly explained, its benefits outweigh the risks. If you think you have found an exception to this rule, contact the Technical Writing team.
GitLab adds all troubleshooting information to the documentation, no matter how unlikely a user is to encounter a situation.
GitLab Support maintains their own troubleshooting content in the GitLab documentation.
The documentation includes all media types
Include any media types/sources if the content is relevant to readers. You can freely include or link presentations, diagrams, and videos. No matter who it was originally composed for, if it is helpful to any of our audiences, we can include it.
- If you use an image that has a separate source file (for example, a vector or diagram format), link the image to the source file so that anyone can update or reuse it.
- Do not copy and paste content from other sources unless it is a limited quotation with the source cited. Typically it is better to either rephrase relevant information in your own words or link out to the other source.
Topic types
In the software industry, it is a best practice to organize documentation in different types. For example:
- Concepts
- Tasks
- Reference
- Troubleshooting
At GitLab, we have not traditionally used topic types. However, we are starting to move in this direction, so we can address these issues:
- Content is hard to find. Our docs are comprehensive and include a large amount of useful information. Topic types create repeatable patterns that make our content easier to scan and parse.
- Content is often written from the contributor's point of view. Our docs are written by contributors. Topic types (tasks specifically) help put information into a format that is geared toward helping others, rather than documenting how a feature was implemented.
GitLab uses these topic type templates.
Link instead of repeating text
Rather than repeating information from another topic, link to the single source of truth and explain why it is important.
Docs-first methodology
We employ a documentation-first methodology. This method ensures the documentation remains a complete and trusted resource, and makes communicating about the use of GitLab more efficient.
- If the answer to a question exists in documentation, share the link to the documentation instead of rephrasing the information.
- When you encounter new information not available in GitLab documentation (for example, when working on a support case or testing a feature), your first step should be to create a merge request (MR) to add this information to the documentation. You can then share the MR to communicate this information.
New information that would be useful toward the future usage or troubleshooting of GitLab should not be written directly in a forum or other messaging system, but added to a documentation MR and then referenced, as described above.
The more we reflexively add information to the documentation, the more the documentation helps others efficiently accomplish tasks and solve problems.
If you have questions when considering, authoring, or editing documentation, ask
the Technical Writing team. They're available on Slack in #docs or in GitLab by
mentioning the writer for
the applicable DevOps stage or group.
Otherwise, forge ahead with your best effort. It does not need to be perfect;
the team is happy to review and improve upon your content. Review the
Documentation guidelines before you begin your first documentation MR.
Maintaining a knowledge base separate from the documentation would be against the documentation-first methodology, because the content would overlap with the documentation.
Markdown
All GitLab documentation is written using Markdown.
The documentation website uses GitLab Kramdown,
a "flavored" Kramdown engine to render pages from Markdown to HTML. The use of Kramdown's
features is limited by our linters, so, use regular Markdown and follow the rules in the
linked style guide. You can't use Kramdown-specific markup (for example, {:.class}).
HTML in Markdown
Hard-coded HTML is valid, although it's discouraged from being used. HTML is permitted if:
- There's no equivalent markup in Markdown.
- Advanced tables are necessary.
- Special styling is required.
- Reviewed and approved by a technical writer.
Markdown Rules
GitLab ensures that the Markdown used across all documentation is consistent, as well as easy to review and maintain, by testing documentation changes with markdownlint. This lint test fails when any document has an issue with Markdown formatting that may cause the page to render incorrectly in GitLab. It also fails when a document has non-standard Markdown (which may render correctly, but is not the current standard for GitLab documentation).
Markdown rule MD044/proper-names (capitalization)
A rule that could cause confusion is MD044/proper-names, as it might not be
immediately clear what caused markdownlint to fail, or how to correct the
failure. This rule checks a list of known words, listed in the .markdownlint.yml
file in each project, to verify proper use of capitalization and backticks.
Words in backticks are ignored by markdownlint.
In general, product names should follow the exact capitalization of the official names of the products, protocols, and so on.
Some examples fail if incorrect capitalization is used:
- MinIO (needs capital
IO) - NGINX (needs all capitals)
- runit (needs lowercase
r)
Additionally, commands, parameters, values, filenames, and so on must be included in backticks. For example:
- "Change the
needskeyword in your.gitlab-ci.yml..."-
needsis a parameter, and.gitlab-ci.ymlis a file, so both need backticks. Additionally,.gitlab-ci.ymlwithout backticks fails markdownlint because it does not have capital G or L.
-
- "Run
git cloneto clone a Git repository..."-
git cloneis a command, so it must be lowercase, while Git is the product, so it must have a capital G.
-
Language
GitLab documentation should be clear and easy to understand.
- Avoid unnecessary words.
- Be clear, concise, and stick to the goal of the topic.
- Write in US English with US grammar. (Tested in
British.yml.)
Capitalization
Headings
Use sentence case. For example:
# Use variables to configure pipelines## Use the To-Do List
UI text
When referring to specific user interface text, like a button label or menu item, use the same capitalization that's displayed in the user interface. Standards for this content are listed in the Pajamas Design System Content section and typically match what's mentioned in this Documentation Style Guide.
If you think the user interface text contains style mistakes, create an issue or an MR to propose a change to the user interface text.
Feature names
- Feature names are typically lowercase.
- Some features require title case, typically nouns that name GitLab-specific capabilities or tools. Features requiring
title case should be:
- Added as a proper name to markdownlint configuration, so that it can be consistently applied across all documentation.
- Added to the word list.
If the term is not in the word list, ask a GitLab Technical Writer for advice.
Do not match the capitalization of terms or phrases on the Features page or features.yml by default.
Other terms
Capitalize names of:
- GitLab product tiers. For example,
GitLab Free and GitLab Ultimate. (Tested in
BadgeCapitalization.yml.) - Third-party organizations, software, and products. For example, Prometheus, Kubernetes, Git, and The Linux Foundation.
- Methods or methodologies. For example, Continuous Integration, Continuous Deployment, Scrum, and Agile.
Follow the capitalization style listed at the authoritative source for the entity, which may use non-standard case styles. For example: GitLab and npm.
Fake user information
You may need to include user information in entries such as a REST call or user profile. Do not use real user information or email addresses in GitLab documentation. For email addresses and names, use:
- Email addresses: Use an email address ending in
example.com. - Names: Use strings like
example_username. Alternatively, use diverse or non-gendered names with common surnames, such asSidney Jones,Zhang Wei, orAlex Garcia.
Fake URLs
When including sample URLs in the documentation, use:
-
example.comwhen the domain name is generic. -
gitlab.example.comwhen referring only to self-managed GitLab instances. Usegitlab.comfor GitLab SaaS instances.
Fake tokens
There may be times where a token is needed to demonstrate an API call using cURL or a variable used in CI. It is strongly advised not to use real tokens in documentation even if the probability of a token being exploited is low.
You can use these fake tokens as examples:
| Token type | Token value |
|---|---|
| Personal access token | <your_access_token> |
| Application ID | 2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6 |
| Application secret | 04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df |
| CI/CD variable | Li8j-mLUVA3eZYjPfd_H |
| Specific runner token | yrnZW46BrtBFqM7xDzE7dddd |
| Shared runner token | 6Vk7ZsosqQyfreAxXTZr |
| Trigger token | be20d8dcc028677c931e04f3871a9b |
| Webhook secret token | 6XhDroRcYPM5by_h-HLY |
| Health check token | Tu7BgjR9qeZTEyRzGG2P |
| Request profile token | 7VgpS4Ax5utVD2esNstz |
Contractions
Contractions are encouraged, and can create a friendly and informal tone, especially in tutorials, instructional documentation, and user interfaces.
Some contractions, however, should be avoided:
| Do not use a contraction | Example | Use instead |
|---|---|---|
| With a proper noun and a verb | The Container Registry's a powerful feature. | The Container Registry is a powerful feature. |
| To emphasize a negative | Don't install X with Y. | Do not install X with Y. |
| In reference documentation | Don't set a limit. | Do not set a limit. |
| In error messages | Requests to localhost aren't allowed. | Requests to localhost are not allowed. |
Acronyms
If you use an acronym, spell it out on first use on a page. You do not need to spell it out more than once on a page. When possible, try to avoid acronyms in headings.
Numbers
When using numbers in text, spell out zero through nine, and use numbers for 10 and greater. For details, see the Microsoft Style Guide.
Text
-
Splitting long lines (preferably up to 100 characters) can make it easier to provide feedback on small chunks of text.
-
Insert an empty line for new paragraphs.
-
Insert an empty line between different markups (for example, after every paragraph, header, list, and so on). Example:
## Header Paragraph. - List item 1 - List item 2
Comments
To embed comments within Markdown, use standard HTML comments that are not rendered when published. Example:
<!-- This is a comment that is not rendered -->Emphasis
Use bold rather than italic to provide emphasis. GitLab uses a sans-serif font and italic text does not stand out as much as it would in a serif font. For details, see Butterick's Practical Typography guide on bold or italic.
You can use italics when you are introducing a term for the first time. Otherwise, use bold.
- Use double asterisks (
**) to mark a word or text in bold (**bold**). - Use underscore (
_) for text in italics (_italic_). - Use greater than (
>) for blockquotes.
Punctuation
Follow these guidelines for punctuation:
- End full sentences with a period.
- Use one space between sentences.
- Do not use semicolons. Use two sentences instead.
- Do not use double spaces. (Tested in
SentenceSpacing.yml.) - Do not use non-breaking spaces. Use standard spaces instead. (Tested in
lint-doc.sh.) - Do not use tabs for indentation. Use spaces instead. You can configure your code editor to output spaces instead of tabs when pressing the tab key.
- Use serial (Oxford) commas before the final and or or in a list of three or more items. (Tested in
OxfordComma.yml.) - Avoid dashes. Use separate sentences, or commas, instead.
- Do not use typographer's ("curly") quotes. Use straight quotes instead. (Tested in
NonStandardQuotes.yml.)
Placeholder text
You might want to provide a command or configuration that uses specific values.
In these cases, use < and >
to call out where a reader must replace text with their own value.
For example:
cp <your_source_directory> <your_destination_directory>Keyboard commands
Use the HTML <kbd> tag when referring to keystroke presses. For example:
To stop the command, press <kbd>Control</kbd>+<kbd>C</kbd>.When the docs are generated, the output is:
To stop the command, press Control+C.
Text entered in the UI
If you want the user to type something in the UI, use backticks. For example:
In the **Commit message** box, type `This is my merge request`.Backticks are more precise than quotes. For example, in this string:
- In the Commit message box, type "This is my merge request."
It's not clear whether the user should include the period in the string.
Lists
- Always start list items with a capital letter, unless they're parameters or commands that are in backticks, or similar.
- Always leave a blank line before and after a list.
- Begin a line with spaces (not tabs) to denote a nested sub-item.
Choose between an ordered or unordered list
Use ordered lists for a sequence of steps. For example:
Follow these steps to do something.
1. First, do the first step.
1. Then, do the next step.
1. Finally, do the last step.Use an unordered lists when the steps do not need to be completed in order. For example:
These things are imported:
- Thing 1
- Thing 2
- Thing 3You can choose to introduce either list with a colon, but you do not have to.
Markup
- Use dashes (
-) for unordered lists instead of asterisks (*). - Prefix
1.to every item in an ordered list. When rendered, the list items display with sequential numbering.
Punctuation
-
Don't add commas (
,) or semicolons (;) to the ends of list items. -
If a list item is a complete sentence (with a subject and a verb), add a period at the end.
-
Majority rules. If the majority of items do not end in a period, do not end any of the items in a period.
-
Separate list items from explanatory text with a colon (
:). For example:The list is as follows: - First item: this explains the first item. - Second item: this explains the second item.
Nesting inside a list item
It's possible to nest items under a list item, so that they render with the same indentation as the list item. This can be done with:
Items nested in lists should always align with the first character of the list
item. In unordered lists (using -), this means two spaces for each level of
indentation:
- Unordered list item 1
A line nested using 2 spaces to align with the `U` above.
- Unordered list item 2
> A quote block that will nest
> inside list item 2.
- Unordered list item 3
```plaintext
a code block that nests inside list item 3
```
- Unordered list item 4
For ordered lists, use three spaces for each level of indentation:
1. Ordered list item 1
A line nested using 3 spaces to align with the `O` above.
1. Ordered list item 2
> A quote block that will nest
> inside list item 2.
1. Ordered list item 3
```plaintext
a code block that nests inside list item 3
```
1. Ordered list item 4
You can nest full lists inside other lists using the same rules as above. If you want to mix types, that's also possible, if you don't mix items at the same level:
1. Ordered list item one.
1. Ordered list item two.
- Nested unordered list item one.
- Nested unordered list item two.
1. Ordered list item three.
- Unordered list item one.
- Unordered list item two.
1. Nested ordered list item one.
1. Nested ordered list item two.
- Unordered list item three.Tables
Tables should be used to describe complex information in a straightforward manner. Note that in many cases, an unordered list is sufficient to describe a list of items with a single, simple description per item. But, if you have data that's best described by a matrix, tables are the best choice.
Creation guidelines
To keep tables accessible and scannable, tables should not have any empty cells. If there is no otherwise meaningful value for a cell, consider entering N/A for 'not applicable' or None.
To help tables be easier to maintain, consider adding additional spaces to the column widths to make them consistent. For example:
| App name | Description | Requirements |
|:---------|:---------------------|:---------------|
| App 1 | Description text 1. | Requirements 1 |
| App 2 | Description text 2. | None |Consider installing a plugin or extension in your editor for formatting tables:
- Markdown Table Prettifier for Visual Studio Code
- Markdown Table Formatter for Sublime Text
- Markdown Table Formatter for Atom
Feature tables
When creating tables of lists of features (such the features available to each role on the Permissions page), use these phrases:
| Option | Markdown | Displayed result |
|---|---|---|
| No | **{dotted-circle}** No |
{dotted-circle} No |
| Yes | **{check-circle}** Yes |
{check-circle} Yes |
Footnotes
To indicate a footnote, use the HTML tag <sup> with a number.
Put the tag at the end of the sentence or term.
For the footnotes below the table, use a bold number followed by a sentence.
For example:
| App name | Description |
|:---------|:---------------------------------|
| App A | Description text. <sup>1</sup> |
| App B | Description text. <sup>2</sup> |
1. This is the footnote.
1. This is the other footnote.This text renders this output:
| App name | Description |
|---|---|
| App A | Description text. 1 |
| App B | Description text. 2 |
- This is the footnote.
- This is the other footnote.
Quotes
Valid for Markdown content only, not for front matter entries:
- Standard quotes: double quotes (
"). Example: "This is wrapped in double quotes". - Quote inside a quote: double quotes (
") wrap single quotes ('). Example: "This sentence 'quotes' something in a quote".
For other punctuation rules, refer to the Pajamas Design System Punctuation section. This is overridden by the documentation-specific punctuation rules.
Headings
In the Markdown document:
- Add one H1 (
#) at the start of the page. Theh1becomes the document<title>. - After the H1, follow the order
h2>h3>h4>h5>h6. - Do not skip a level. For example:
h2>h4. - Leave one blank line before and after the heading.
For the heading text, do:
- Be clear and direct. Make every word count.
- Use active verbs for tasks. For example,
Configure GDKinstead ofConfiguring GDK. - Talk about what the product does, realistically but from a positive perspective. Instead of
Limitations, move the content near other similar information. If you must, you can use the titleKnown issues. - Use articles and prepositions.
- Add the product badge that corresponds to the license tier.
- Follow capitalization guidelines.
For the heading text, do not:
- Use generic words like
OvervieworUse cases. Instead, incorporate the information under a concept heading. - Use
How it works. Incorporate this information under a concept, or use a noun followed byworkflow. For example,Merge request workflow. - Use
Important Notes. Incorporate this information closer to where it belongs. - Use numbers to indicate steps. If the numbers change, the anchor links changes, which eventually leads to dead links. If you think you must add numbers in headings, at least discuss it with a writer in the merge request.
- Use words that might change in the future. Changing a heading changes its anchor URL, which affects other linked pages.
- Repeat text from earlier headings. For example, instead of
Troubleshooting merge requests, useTroubleshooting. - Use links.
Anchor links
Headings generate anchor links when rendered. ## This is an example generates
the anchor #this-is-an-example.
NOTE:
Introduced in
GitLab 13.4, product badges used in headings aren't
included in the generated anchor links. For example, when you link to
## This is an example **(FREE)**, use the anchor #this-is-an-example.
Keep in mind that the GitLab user interface links to many documentation pages
and anchor links to take the user to the right spot. When you change
a heading, search doc/*, app/views/*, and ee/app/views/* for the old
anchor. If you do not fix these links, the ui-docs-lint job
in your merge request fails.
Important:
- Avoid crosslinking documentation to headings unless you need to link to a specific section of the document. This avoids breaking anchors in the future in case the heading is changed.
- If possible, avoid changing headings, because they're not only linked internally. There are various links to GitLab documentation on the internet, such as tutorials, presentations, StackOverflow posts, and other sources.
- Do not link to
h1headings.
Note that with Kramdown, it's possible to add a custom ID to an HTML element
with Markdown markup, but they don't work in /help. Because of this, don't use
this option.
Links
Links are important in GitLab documentation. Use links instead of summarizing to help preserve a single source of truth in GitLab documentation.
We include guidance for links in these categories:
- How to set up anchor links for headings.
- How to set up criteria for configuring a link.
- What to set up when linking to a
helppage. - How to set up links to internal documentation for cross-references.
- How to set up links to external documentation for authoritative sources.
- When to use links requiring permissions.
- How to set up a link to a video.
- How to include links with version text.
- How to link to specific lines of code
Basic link criteria
-
Use inline link Markdown markup
[Text](https://example.com). It's easier to read, review, and maintain. Do not use[Text][identifier]reference-style links. -
Use meaningful anchor text. For example, instead of writing something like
Read more about merge requests [here](LINK), writeRead more about [merge requests](LINK).
Links to internal documentation
NOTE: Internal refers to documentation in the same project. When linking to documentation in separate projects (for example, linking to Omnibus documentation from GitLab documentation), you must use absolute URLs.
Do not use absolute URLs like https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/index.html to
cross-link to other documentation in the same project. Use relative links to
the file, like ../index.md. (These are converted to HTML when the site is
rendered.)
Relative linking enables crosslinks to work:
- in Review Apps, local previews, and
/help. - when working on the documentation locally, so you can verify that they work as early as possible in the process.
- in the GitLab user interface when browsing doc files in their respective
repositories. For example, the links displayed at
https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/doc/README.md.
To link to internal documentation:
-
Use relative links to Markdown files in the same repository.
-
Do not use absolute URLs or URLs from
docs.gitlab.com. -
Use
../to navigate to higher-level directories. -
Don't prepend
./to links to files or directories. To link to a file in the same directory or one of its sub-directories, use the syntaxpath/to/file.md. -
Don't link relative to root. For example,
/ee/user/gitlab_com/index.md.Don't:
https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/geo/replication/troubleshooting.html/ee/administration/geo/replication/troubleshooting.md./troubleshooting.md
Do:
../../geo/replication/troubleshooting.md -
Always add the filename
file.mdat the end of the link with the.mdextension, not.html.Don't:
../../merge_requests/../../issues/tags.html../../issues/tags.html#stages
Do:
../../merge_requests/index.md../../issues/tags.md../../issues/tags.md#stagesissues/tags.md
NOTE:
Using the Markdown extension is necessary for the /help
section of GitLab.
Links to external documentation
When describing interactions with external software, it's often helpful to include links to external documentation. When possible, make sure that you're linking to an authoritative source. For example, if you're describing a feature in Microsoft's Active Directory, include a link to official Microsoft documentation.
Authoritative sources
When citing external information, use sources that are written by the people who created the item or product in question. These sources are the most likely to be accurate and remain up to date.
Examples of authoritative sources include:
- Specifications, such as a Request for Comments document from the Internet Engineering Task Force.
- Official documentation for a product. For example, if you're setting up an interface with the Google OAuth 2 authorization server, include a link to Google's documentation.
- Official documentation for a project. For example, if you're citing NodeJS functionality, refer directly to NodeJS documentation.
- Books from an authoritative publisher.
Examples of sources to avoid include:
- Personal blog posts.
- Wikipedia.
- Non-trustworthy articles.
- Discussions on forums such as Stack Overflow.
- Documentation from a company that describes another company's product.
While many of these sources to avoid can help you learn skills and or features, they can become obsolete quickly. Nobody is obliged to maintain any of these sites. Therefore, we should avoid using them as reference literature.
NOTE: Non-authoritative sources are acceptable only if there is no equivalent authoritative source. Even then, focus on non-authoritative sources that are extensively cited or peer-reviewed.
Links requiring permissions
Don't link directly to:
- Confidential issues.
- Project features that require special permissions to view.
These fail for:
- Those without sufficient permissions.
- Automated link checkers.
Instead:
- To reduce confusion, mention in the text that the information is either:
- Contained in a confidential issue.
- Requires special permission to a project to view.
- Provide a link in back ticks (
`) so that those with access to the issue can navigate to it.
Example:
For more information, see the [confidential issue](../../../user/project/issues/confidential_issues.md) `https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss/-/issues/<issue_number>`.Link to specific lines of code
When linking to specific lines in a file, link to a commit instead of to the branch. Lines of code change over time. Linking to a line by using the commit link ensures the user lands on the line you're referring to. The Permalink button, displayed when viewing a file in a project, provides a link to the most recent commit of that file.
- Do:
[link to line 3](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/11f17c56d8b7f0b752562d78a4298a3a95b5ce66/.gitlab/issue_templates/Feature%20proposal.md#L3) - Don't:
[link to line 3](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/.gitlab/issue_templates/Feature%20proposal.md#L3).
If that linked expression has changed line numbers due to additional commits, you can still search the file for that query. In this case, update the document to ensure it links to the most recent version of the file.
Navigation
When documenting how to navigate through the GitLab UI:
- Always use location, then action.
- From the Visibility dropdown list (location), select Public (action).
- Be brief and specific. For example:
- Do: Select Save.
- Do not: Select Save for the changes to take effect.
- If a step must include a reason, start the step with it. This helps the user scan more quickly.
- Do: To view the changes, in the merge request, select the link.
- Do not: Select the link in the merge request to view the changes.
Names for menus
Use these terms when referring to the main GitLab user interface elements:
- Top bar: This is the top bar that spans the width of the user interface. It includes the menu, the GitLab logo, search field, counters, and the user's avatar.
- Left sidebar: This is the navigation sidebar on the left of the user interface, specific to the project or group.
- Right sidebar: This is the navigation sidebar on the right of the user interface, specific to the open issue, merge request, or epic.
Names for UI elements
UI elements, like button and checkbox names, should be bold. Guidance for each individual UI element is in the word list.
How to write navigation task steps
To be consistent, use these templates when you write navigation steps in a task topic.
To open project settings:
1. On the top bar, select **Menu > Projects** and find your project.
1. On the left sidebar, select **Settings > CI/CD**.
1. Expand **General pipelines**.To open group settings:
1. On the top bar, select **Menu > Groups** and find your group.
1. On the left sidebar, select **Settings > CI/CD**.
1. Expand **General pipelines**.To open the Admin Area:
1. On the top bar, select **Menu > Admin**.To select your avatar:
1. On the top bar, in the top right corner, select your avatar.To save the selection in some dropdown lists:
1. Go to your issue.
1. On the right sidebar, in the **Iteration** section, select **Edit**.
1. From the dropdown list, select the iteration to associate this issue with.
1. Select any area outside the dropdown list.Optional steps
If a step is optional, start the step with the word Optional followed by a period.
For example:
1. Optional. Enter a description for the job.Documenting multiple fields at once
If the UI text sufficiently explains the fields in a section, do not include a task step for every field. Instead, summarize multiple fields in a single task step.
Use the phrase Complete the fields.
For example:
- On the top bar, select Menu > Projects and find your project.
- On the left sidebar, select Settings > Repository.
- Expand Push rules.
- Complete the fields.
If you are documenting multiple fields and only one field needs explanation, do it in the same step:
- Expand Push rules.
- Complete the fields. Branch name must be a regular expression.
To describe multiple fields, use bullets:
- Expand General pipelines.
- Complete the fields.
- Branch name must be a regular expression.
- User must be a user with at least the Maintainer role.
Images
Images, including screenshots, can help a reader better understand a concept. However, they should be used sparingly because:
- They tend to become out-of-date.
- They are difficult and expensive to localize.
- They cannot be read by screen readers.
When needed, use images to help the reader understand:
- Where they are in a complicated process.
- How they should interact with the application.
Capture the image
When you take screenshots:
-
Ensure it provides value. Don't use
lorem ipsumtext. Try to replicate how the feature would be used in a real-world scenario, and use realistic text. - Capture only the relevant UI. Don't include unnecessary white space or areas of the UI that don't help illustrate the point. The sidebars in GitLab can change, so don't include them in screenshots unless absolutely necessary.
- Keep it small. If you don't need to show the full width of the screen, don't. Reduce the size of your browser window as much as possible to keep elements close together and reduce empty space. Try to keep the screenshot dimensions as small as possible.
- Review how the image renders on the page. Preview the image locally or use the review app in the merge request. Make sure the image isn't blurry or overwhelming.
- Be consistent. Coordinate screenshots with the other screenshots already on a documentation page for a consistent reading experience. Ensure your navigation theme is Indigo and the syntax highlighting theme is Light. These are the default preferences.
Add callouts
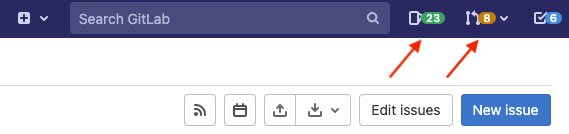
If you need to emphasize an area in a screenshot, use an arrow.
- For color, use
#EE2604. If you use the Preview application on macOS, this is the default red. - For the line width, use 3 pt. If you use the Preview application on macOS, this is the third line in the list.
- Use the arrow style shown in the following image.
- If you have multiple arrows, make them parallel when possible.
Save the image
- Resize any wide or tall screenshots if needed, but make sure the screenshot is still clear after being resized and compressed.
- All images must be compressed to 100KB or less. In many cases, 25-50KB or less is often possible without reducing image quality.
- Save the image with a lowercase filename that's descriptive of the feature
or concept in the image:
- If the image is of the GitLab interface, append the GitLab version to the filename,
based on this format:
image_name_vX_Y.png. For example, for a screenshot taken from the pipelines page of GitLab 11.1, a valid name ispipelines_v11_1.png. - If you're adding an illustration that doesn't include parts of the user interface,
add the release number corresponding to the release the image was added to.
For an MR added to 11.1's milestone, a valid name for an illustration is
devops_diagram_v11_1.png.
- If the image is of the GitLab interface, append the GitLab version to the filename,
based on this format:
- Place images in a separate directory named
img/in the same directory where the.mddocument that you're working on is located. - Consider using PNG images instead of JPEG.
- Compress GIFs with https://ezgif.com/optimize or similar tool.
- Images should be used (only when necessary) to illustrate the description of a process, not to replace it.
- See also how to link and embed videos to illustrate the documentation.
Add the image link to content
The Markdown code for including an image in a document is:

The image description is the alt text for the rendered image on the documentation site. For accessibility and SEO, use descriptions that:
- Are accurate, succinct, and unique.
- Don't use image of or graphic of to describe the image.
Compress images
You should always compress any new images you add to the documentation. One
known tool is pngquant, which is cross-platform and
open source. Install it by visiting the official website and following the
instructions for your OS.
If you use macOS and want all screenshots to be compressed automatically, read One simple trick to make your screenshots 80% smaller.
GitLab has a Ruby script
that you can use to simplify the manual process. In the root directory of your local
copy of https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab, run in a terminal:
-
Before compressing, if you want, check that all documentation PNG images have been compressed:
bin/pngquant lint -
Compress all documentation PNG images using
pngquant:bin/pngquant compress -
Compress specific files:
bin/pngquant compress doc/user/img/award_emoji_select.png doc/user/img/markdown_logo.png -
Compress all PNG files in a specific directory:
bin/pngquant compress doc/user/img
Animated images
Sometimes an image with animation (such as an animated GIF) can help the reader understand a complicated interaction with the user interface.
However, you should use them sparingly and avoid them when you can. Do not use them to replace written descriptions of processes or the product.
If you include an animated image, follow the same size and naming conventions we use for images. If the animated image loops, add at least a three second pause to the end of the loop.
Videos
Adding GitLab YouTube video tutorials to the documentation is highly encouraged, unless the video is outdated. Videos should not replace documentation, but complement or illustrate it. If content in a video is fundamental to a feature and its key use cases, but isn't adequately covered in the documentation, you should:
- Add this detail to the documentation text.
- Create an issue to review the video and update the page.
Do not upload videos to the product repositories. Link or embed them instead.
Link to video
To link out to a video, include a YouTube icon so that readers can scan the page for videos before reading:
<i class="fa fa-youtube-play youtube" aria-hidden="true"></i>
For an overview, see [Video Title](link-to-video).You can link any up-to-date video that's useful to the GitLab user.
Embed videos
Introduced in GitLab 12.1.
The GitLab documentation site supports embedded videos.
You can embed videos from the official YouTube account for GitLab only. For videos from other sources, link them instead.
In most cases, link to a video, because embedded videos take up a lot of space on the page and can be distracting to readers.
To embed a video:
- Copy the code from this procedure and paste it into your Markdown file. Leave a blank line above and below it. Do not edit the code (don't remove or add any spaces).
- In YouTube, visit the video URL you want to display. Copy the regular URL
from your browser (
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VIDEO-ID) and replace the video title and link in the line under<div class="video-fallback">. - In YouTube, select Share, and then select Embed.
- Copy the
<iframe>source (src) URL only (https://www.youtube.com/embed/VIDEO-ID), and paste it, replacing the content of thesrcfield in theiframetag.
leave a blank line here
<div class="video-fallback">
See the video: <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MqL6BMOySIQ">Video title</a>.
</div>
<figure class="video-container">
<iframe src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/MqL6BMOySIQ" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="true"> </iframe>
</figure>
leave a blank line hereThis is how it renders on the GitLab documentation site:
Notes:
- The
figuretag is required for semantic SEO and thevideo_containerclass is necessary to make sure the video is responsive and displays on different mobile devices.- The
<div class="video-fallback">is a fallback necessary for/help, because the GitLab Markdown processor doesn't support iframes. It's hidden on the documentation site, but is displayed by/help.
Code blocks
-
Always wrap code added to a sentence in inline code blocks (
`). For example,.gitlab-ci.yml,git add .,CODEOWNERS, oronly: [main]. File names, commands, entries, and anything that refers to code should be added to code blocks. To make things easier for the user, always add a full code block for things that can be useful to copy and paste, as they can do it with the button on code blocks. -
HTTP methods (
HTTP POST) and HTTP status codes, both full (404 File Not Found) and abbreviated (404), should be wrapped in inline code blocks when used in sentences. For example: Send aDELETErequest to delete the runner. Send aPOSTrequest to create one. -
Add a blank line above and below code blocks.
-
When providing a shell command and its output, prefix the shell command with
$and leave a blank line between the command and the output. -
When providing a command without output, don't prefix the shell command with
$. -
If you need to include triple backticks inside a code block, use four backticks for the code block fences instead of three.
-
For regular fenced code blocks, always use a highlighting class corresponding to the language for better readability. Examples:
```ruby Ruby code ``` ```javascript JavaScript code ``` ```markdown [Markdown code example](example.md) ``` ```plaintext Code or text for which no specific highlighting class is available. ```
Syntax highlighting is required for fenced code blocks added to the GitLab documentation. Refer to this table for the most common language classes, or check the complete list of available language classes:
| Preferred language tags | Language aliases and notes |
|---|---|
asciidoc |
|
dockerfile |
Alias: docker. |
elixir |
|
erb |
|
golang |
Alias: go. |
graphql |
|
haml |
|
html |
|
ini |
For some simple configuration files that are not in TOML format. |
javascript |
Alias js. |
json |
|
markdown |
Alias: md. |
mermaid |
|
nginx |
|
perl |
|
php |
|
plaintext |
Examples with no defined language, such as output from shell commands or API calls. If a code block has no language, it defaults to plaintext. Alias: text. |
prometheus |
Prometheus configuration examples. |
python |
|
ruby |
Alias: rb. |
shell |
Aliases: bash or sh. |
sql |
|
toml |
Runner configuration examples, and other TOML-formatted configuration files. |
typescript |
Alias: ts. |
xml |
|
yaml |
Alias: yml. |
For a complete reference on code blocks, see the Kramdown guide.
GitLab SVG icons
Introduced in GitLab 12.7.
You can use icons from the GitLab SVG library
directly in the documentation. For example, **{tanuki}** renders as: {tanuki}.
In most cases, you should avoid using the icons in text. However, you can use an icon when hover text is the only available way to describe a UI element. For example, Delete or Edit buttons often have hover text only.
When you do use an icon, start with the hover text and follow it with the SVG reference in parentheses.
- Avoid:
Select **{pencil}** **Edit**.This generates as: Select {pencil} Edit. - Use instead:
Select **Edit** (**{pencil}**).This generates as: Select Edit ({pencil}).
Do not use words to describe the icon:
- Avoid:
Select **Erase job log** (the trash icon). - Use instead:
Select **Erase job log** (**{remove}**).This generates as: Select Erase job log ({remove}).
Alert boxes
Use alert boxes to call attention to information. Use them sparingly, and never have an alert box immediately follow another alert box.
Alert boxes are generated when one of these words is followed by a line break:
FLAG:NOTE:WARNING:-
INFO:(Marketing only) DISCLAIMER:
For example:
NOTE:
This is something to note.To display an alert box for multiple paragraphs, lists, or headers, use blockquotes instead.
Alert boxes render only on the GitLab documentation site (https://docs.gitlab.com). In the GitLab product help, alert boxes appear as plain text.
Flag
Use this alert type to describe a feature's availability. For information about how to format
FLAG alerts, see Document features deployed behind feature flags.
Note
Use notes sparingly. Too many notes can make topics difficult to scan.
Instead of adding a note:
- Re-write the sentence as part of a paragraph.
- Put the information into its own paragraph.
- Put the content under a new subheading.
If you must use a note, use this format:
NOTE:
This is something to note.It renders on the GitLab documentation site as:
NOTE: This is something to note.
Warning
Use a warning to indicate deprecated features, or to provide a warning about procedures that have the potential for data loss.
WARNING:
This is something to be warned about.It renders on the GitLab documentation site as:
WARNING: This is something to be warned about.
Info
The Marketing team uses the INFO alert to add information relating
to sales and marketing efforts.
The text in an INFO: alert always renders in a floating text box to the right of the text around it.
To view the rendered GitLab docs site, check the review app in the MR. You might need to move the text up or down
in the surrounding text, depending on where you'd like to floating box to appear.
For example, if your page has text like this:
This is an introductory paragraph. GitLab uses the SSH protocol to securely communicate with Git.
When you use SSH keys to authenticate to the GitLab remote server,
you don't need to supply your username and password each time.
INFO:
Here is some information. This information is an important addition to how you
work with GitLab and you might want to consider it.
And here is another paragraph. GitLab uses the SSH protocol to securely communicate with Git.
When you use SSH keys to authenticate to the GitLab remote server,
you don't need to supply your username and password each time.
And here is another paragraph. GitLab uses the SSH protocol to securely communicate with Git.
When you use SSH keys to authenticate to the GitLab remote server,
you don't need to supply your username and password each time.It renders on the GitLab documentation site as:
This is an introductory paragraph. GitLab uses the SSH protocol to securely communicate with Git. When you use SSH keys to authenticate to the GitLab remote server, you don't need to supply your username and password each time.
INFO: Here is some information. This information is an important addition to how you work with GitLab and you might want to consider it.
And here is another paragraph. GitLab uses the SSH protocol to securely communicate with Git. When you use SSH keys to authenticate to the GitLab remote server, you don't need to supply your username and password each time.
And here is another paragraph. GitLab uses the SSH protocol to securely communicate with Git. When you use SSH keys to authenticate to the GitLab remote server, you don't need to supply your username and password each time.
Disclaimer
Use to describe future functionality only. For more information, see Legal disclaimer for future features.
Blockquotes
For highlighting a text inside a blockquote, use this format:
> This is a blockquote.It renders on the GitLab documentation site as:
This is a blockquote.
If the text spans multiple lines, you can split them.
For multiple paragraphs, use the symbol > before every line:
> This is the first paragraph.
>
> This is the second paragraph.
>
> - This is a list item
> - Second item in the listIt renders on the GitLab documentation site as:
This is the first paragraph.
This is the second paragraph.
- This is a list item
- Second item in the list
Terms
To maintain consistency through GitLab documentation, use these styles and terms.
Describe UI elements
Follow these styles when you're describing user interface elements in an application:
- For elements with a visible label, use that label in bold with matching case.
For example,
Select **Cancel**. - For elements with a tooltip or hover label, use that label in bold with
matching case. For example,
Select **Add status emoji**.
GitLab versions
GitLab product documentation pages (not including Contributor and Development
pages in the /development directory) can include version information to help
users be aware of recent improvements or additions.
The GitLab Technical Writing team determines which versions of documentation to display on this site based on the GitLab Statement of Support.
View older GitLab documentation versions
Older versions of GitLab may no longer have documentation available from docs.gitlab.com.
If documentation for your version is no longer available from docs.gitlab.com, you can still view a
tagged and released set of documentation for your installed version:
- In the documentation archives.
- At the
/helpURL of your GitLab instance. - In the documentation repository based on the respective branch (for example, the 13.2 branch).
Where to put version text
When a feature is added or updated, you can include its version information either as a Version history item or as an inline text reference.
Version text in the Version History
If all content in a section is related, add version text after the header for the section. The version information must:
- Be surrounded by blank lines.
- Start with
>. If there are multiple bullets, each line must start with> -. - The string must include these words in this order (capitalization doesn't matter):
-
introduced,enabled,deprecated,changed,moved,recommended(as in the feature flag documentation),removed, orrenamed -
inorto GitLab
-
- Whenever possible, include a link to the completed issue, merge request, or epic that introduced the feature. An issue is preferred over a merge request, and a merge request is preferred over an epic.
- Do not include information about the tier, unless documenting a tier change
(for example,
Feature X [moved](issue-link) to Premium in GitLab 19.2). - Do not link to the pricing page. The tier is provided by the product badge on the heading.
## Feature name
> [Introduced](<link-to-issue>) in GitLab 11.3.
This feature does something.
## Feature name 2
> - [Introduced](<link-to-issue>) in GitLab 11.3.
> - [Enabled by default](<link-to-issue>) in GitLab 11.4.
This feature does something else.If you're documenting elements of a feature, start with the feature name or a gerund:
> - Notifications for expiring tokens [introduced](<link-to-issue>) in GitLab 11.3.
> - Creating an issue from an issue board [introduced](<link-to-issue>) in GitLab 13.1.If a feature is moved to another tier:
> - [Moved](<link-to-issue>) from GitLab Ultimate to GitLab Premium in 11.8.
> - [Moved](<link-to-issue>) from GitLab Premium to GitLab Free in 12.0.Inline version text
If you're adding content to an existing topic, you can add version information inline with the existing text.
In this case, add ([introduced/deprecated](<link-to-issue>) in GitLab X.X).
Including the issue link is encouraged, but isn't a requirement. For example:
The voting strategy in GitLab 13.4 and later requires the primary and secondary
voters to agree.Deprecated features
When a feature is deprecated, add (DEPRECATED) to the page title or to
the heading of the section documenting the feature, immediately before
the tier badge:
<!-- Page title example: -->
# Feature A (DEPRECATED) **(ALL TIERS)**
<!-- Doc section example: -->
## Feature B (DEPRECATED) **(PREMIUM SELF)**Add the deprecation to the version history note (you can include a link to a replacement when available):
> - [Deprecated](<link-to-issue>) in GitLab 11.3. Replaced by [meaningful text](<link-to-appropriate-documentation>).You can also describe the replacement in surrounding text, if available. If the deprecation isn't obvious in existing text, you may want to include a warning:
WARNING:
This feature was [deprecated](link-to-issue) in GitLab 12.3 and replaced by
[Feature name](link-to-feature-documentation).If you add (DEPRECATED) to the page's title and the document is linked from the docs
navigation, either remove the page from the nav or update the nav item to include the
same text before the feature name:
- doc_title: (DEPRECATED) Feature AIn the first major GitLab version after the feature was deprecated, be sure to remove information about that deprecated feature.
End-of-life for features or products
When a feature or product enters its end-of-life, indicate its status by creating a warning alert directly after its relevant header. If possible, link to its deprecation and removal issues.
For example:
WARNING:
This feature is in its end-of-life process. It is [deprecated](link-to-issue)
in GitLab X.X, and is planned for [removal](link-to-issue) in GitLab X.X.After the feature or product is officially deprecated and removed, remove its information from the GitLab documentation.
Versions in the past or future
When describing functionality available in past or future versions, use:
- Earlier, and not older or before.
- Later, and not newer or after.
For example:
- Available in GitLab 13.1 and earlier.
- Available in GitLab 12.4 and later.
- In GitLab 12.2 and earlier, ...
- In GitLab 11.6 and later, ...
Promising features in future versions
Do not promise to deliver features in a future release. For example, avoid phrases like, "Support for this feature is planned."
We cannot guarantee future feature work, and promises like these can raise legal issues. Instead, say that an issue exists. For example:
- Support for improvements is tracked
[in this issue](LINK). - You cannot do this thing, but
[an issue exists](LINK)to change this behavior.
You can say that we plan to remove a feature.
Legal disclaimer for future features
If you must write about features we have not yet delivered, put this exact disclaimer near the content it applies to.
DISCLAIMER:
This page contains information related to upcoming products, features, and functionality.
It is important to note that the information presented is for informational purposes only.
Please do not rely on this information for purchasing or planning purposes.
As with all projects, the items mentioned on this page are subject to change or delay.
The development, release, and timing of any products, features, or functionality remain at the
sole discretion of GitLab Inc.It renders on the GitLab documentation site as:
DISCLAIMER: This page contains information related to upcoming products, features, and functionality. It is important to note that the information presented is for informational purposes only. Please do not rely on this information for purchasing or planning purposes. As with all projects, the items mentioned on this page are subject to change or delay. The development, release, and timing of any products, features, or functionality remain at the sole discretion of GitLab Inc.
If all of the content on the page is not available, use the disclaimer once at the top of the page.
If the content in a topic is not ready, use the disclaimer in the topic.
Removing versions after each major release
When a major GitLab release occurs, we remove all references to now-unsupported versions. This removal includes version-specific instructions. For example, if GitLab version 12.1 and later are supported, instructions for users of GitLab 11 should be removed.
View the list of supported versions.
To view historical information about a feature, review GitLab release posts, or search for the issue or merge request where the work was done.
Products and features
Refer to the information in this section when describing products and features in the GitLab product documentation.
Avoid line breaks in names
If a feature or product name contains spaces, don't split the name with a line break. When names change, it is more complicated to search or grep text that has line breaks.
Product tier badges
Tier badges are displayed as orange text next to a heading. These badges link to the GitLab pricing page. For example:
You must assign a tier badge:
- To all H1 topic headings.
- To topic headings that don't apply to the same tier as the H1.
To add a tier badge to a heading, add the relevant tier badge after the heading text. For example:
# Heading title **(FREE)**Do not add tier badges inline with other text, except for API attributes. The single source of truth for a feature should be the heading where the functionality is described.
Available product tier badges
| Tier in which feature is available | Tier badge |
|---|---|
| GitLab Free self-managed and SaaS, and higher tiers | **(FREE)** |
| GitLab Premium self-managed and SaaS, and their higher tiers | **(PREMIUM)** |
| GitLab Ultimate self-managed and SaaS | **(ULTIMATE)** |
| Only GitLab Free self-managed and higher tiers (no SaaS-based tiers) | **(FREE SELF)** |
| Only GitLab Premium self-managed and higher tiers (no SaaS-based tiers) | **(PREMIUM SELF)** |
| Only GitLab Ultimate self-managed (no SaaS-based tiers) | **(ULTIMATE SELF)** |
| Only GitLab Free SaaS and higher tiers (no self-managed instances) | **(FREE SAAS)** |
| Only GitLab Premium SaaS and higher tiers (no self-managed instances) | **(PREMIUM SAAS)** |
| Only GitLab Ultimate SaaS (no self-managed instances) | **(ULTIMATE SAAS)** |
Topics that mention the gitlab.rb file are referring to
self-managed instances of GitLab. To prevent confusion, include the relevant TIER SELF
tier badge on the highest applicable heading level on
the page.
Specific sections
Certain styles should be applied to specific sections. Styles for specific sections are outlined in this section.
GitLab restart
When a restart or reconfigure of GitLab is required, avoid duplication by linking
to doc/administration/restart_gitlab.md
with text like this, replacing 'reconfigure' with 'restart' as needed:
Save the file and [reconfigure GitLab](../../../administration/restart_gitlab.md)
for the changes to take effect.If the document resides outside of the doc/ directory, use the full path
instead of the relative link:
https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/restart_gitlab.html.
Installation guide
In step 2 of the installation guide, we install Ruby from source. To update the guide for a new Ruby version:
- Change the version throughout the code block.
- Replace the sha256sum. It's available on the downloads page of the Ruby website.
Configuration documentation for source and Omnibus installations
GitLab supports two installation methods: installations from source, and Omnibus packages. Possible configuration settings include:
- Settings that touch configuration files in
config/. - NGINX settings.
- Other settings in
lib/support/.
Configuration procedures can require users to edit configuration files, reconfigure
GitLab, or restart GitLab. Use these styles to document these steps, replacing
PATH/TO with the appropriate path:
**For Omnibus installations**
1. Edit `/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb`:
```ruby
external_url "https://gitlab.example.com"
```
1. Save the file and [reconfigure](PATH/TO/administration/restart_gitlab.md#omnibus-gitlab-reconfigure)
GitLab for the changes to take effect.
---
**For installations from source**
1. Edit `config/gitlab.yml`:
```yaml
gitlab:
host: "gitlab.example.com"
```
1. Save the file and [restart](PATH/TO/administration/restart_gitlab.md#installations-from-source)
GitLab for the changes to take effect.In this case:
- Bold the installation method's name.
- Separate the methods with three dashes (
---) to create a horizontal line. - Indent the code blocks to line up with the list item they belong to..
- Use the appropriate syntax highlighting for each code block.
- Use the GitLab Restart section to explain any required restart or reconfigure of GitLab.
Feature flags
Learn how to document features deployed behind flags. For guidance on developing GitLab with feature flags, see Feature flags in development of GitLab.